beta oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids|how does beta oxidation work : Manila Fatty acids, obtained from the breakdown of triglycerides and other lipids, are oxidized through a series of reactions known as β . Navigate the world of roulette online gambling with ease. Our article spotlights the top sites of 2024, focusing on bonuses, quick payouts, and immersive gameplay. Whether you’re looking to play for free or for real money, we guide you to the best online roulette experiences available.PinaySite.com is updated with the latest Pinay Porn and rare Pinay Sex Scandal. Visit us to enjoy Latest Trending and New Filipina Viral Sex videos.
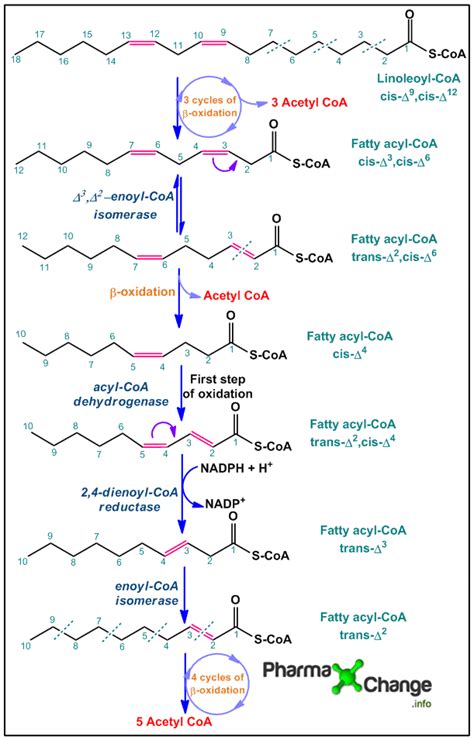
beta oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids,Let us consider an example of monounsaturated fatty acid such as oleic acid and a polyunsaturated fatty acid such as linolenic acid. Oleic acid is an 18 carbon chain length fatty acid with a cis double bond present between the ninth and the tenth carbons. Linolenic acid is an 18 carbon chain length . Tingnan ang higit pa

Fatty acids occur as saturated and unsaturated (with one or more double bonds) fatty acids. Fatty acids majorly in triacylglycerols and phospholipids are present as unsaturated fatty acids in plants and animals.Saturated fatty acids undergo β . Tingnan ang higit paβ-Oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids poses a problem since the location of a cis-bond can prevent the formation of a trans-Δ bond which is essential for continuation of β-Oxidation as this conformation is ideal for enzyme catalysis. This is handled by additional two enzymes, Enoyl CoA isomerase and 2,4 Dienoyl CoA reductase.
Fatty acids, obtained from the breakdown of triglycerides and other lipids, are oxidized through a series of reactions known as β .
beta oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids As noted above, oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids requires two additional enzymes to the complement of enzymes for beta oxidation. If the beta oxidation of the fatty acid produces an . Beta oxidation requires specific enzymes to carry out the metabolism of fatty acids. For saturated fatty acids, such as palmitate (16:0) and stearate (18:0), a base set of enzymes catalyze the reactions to . Understand the catabolism of fatty acids, i.e., \(\beta\)-oxidation of fatty acids, the reactions involved in the process, the number of cycles needed, and the calculation of ATP yield per fatty acid.how does beta oxidation workBeta oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids. In the oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids, most of the reactions are the same as those for saturated fatty acids, only two additional enzymes an isomerase and a .beta oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids how does beta oxidation workBeta oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids. In the oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids, most of the reactions are the same as those for saturated fatty acids, only two additional enzymes an isomerase and a .A revised pathway (the reductase-dependent pathway) by which polyunsaturated fatty acids are β-oxidized is presented. This pathway requires the involvement of a NADPH . In contrast to the oxidation of short and medium-chain fatty acids, which under beta-oxidation require four different discrete enzymes, the oxidation of very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFs) is carried out by .
The end result of these broken bonds are a glycerol molecule and three fatty acids in the case of triglycerides. Other lipids are capable of being degraded as well. Key molecules .
The energy released by fatty acid oxidation is thus conserved as ATP. Steps in beta-oxidation of fatty acids: 1. Step I: Activation of a fatty acid by conversion to a fatty acyl CoA. After fatty . The chemistry, biochemistry, pharmacology and molecular biology of oxylipins (defined as a family of oxygenated natural products that are formed from unsaturated fatty acids by pathways involving at least one step of dioxygen-dependent oxidation) are complex and occasionally contradictory subjects that continue to develop at an . Beta oxidation is a metabolic process involving multiple steps by which fatty acid molecules are broken down to produce energy. More specifically, beta oxidation consists in breaking down long fatty .A revised pathway (the reductase-dependent pathway) by which polyunsaturated fatty acids are β-oxidized is presented. This pathway requires the involvement of a NADPH-dependent 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase in addition to Δ3 -cis- Δ2 -trans- enoyl - CoA isomerase and the enzymes necessary for the oxidation of saturated fatty acids.Fatty acid β-oxidation is the process by which fatty acids are broken down to produce energy. Fatty acids primarily enter a cell via fatty acid protein transporters on the cell surface. Once inside, FACS adds a CoA group to the fatty acid. CPT1 then converts the long-chain acyl-CoA to long-chain acylcarnitine.

This video explains the concept behind the oxidation process of PUFA and MUFA and compares it to the oxidation process of saturated fatty acids A revised pathway (the reductase-dependent pathway) by which polyunsaturated fatty acids are β-oxidized is presented. This pathway requires the involvement of a NADPH-dependent 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase in addition to Δ3 -cis- Δ2 -trans- enoyl - CoA isomerase and the enzymes necessary for the oxidation of saturated .Saturated fatty acids are degraded by β-oxidation to yield acetyl CoA which is used as an energy source in mitochondria. . Unsaturated fatty acids are the cellular macromolecules most sensitive to oxygen radical damage, owing to the presence of highly unstable electrons near their double bonds, and their sensitivity to lipid peroxidation .
Beta-Oxidation is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. The best source of energy for eukaryotic organisms are fats. Glucose offers a ratio 6.3 moles of ATP per carbon while saturated fatty acids offer 8.1 ATP per carbon. Also the complete oxidation of .. Abstract. The development of detection technology prompts the need to elaborate on the theory behind the oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids. This study integrates the detection of monounsaturated fatty acid oxidation at 60 °C with computational simulations to provide an advanced theoretical basis for the formation of . This document summarizes fatty acid oxidation through beta-oxidation. It discusses how fatty acids are broken down into acetyl-CoA in the mitochondria, generating energy in the form of ATP. Key points covered include the carnitine shuttle transport system, reactions of beta-oxidation, and oxidation of odd-chain and unsaturated fatty acids.
Unsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids also are degraded by β-oxidation.However, additional reactions are required to metabolize pre-existing double bonds that would otherwise interfere with the complete β-oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids.All double bonds found in unsaturated fatty acids can be classified as either odd- or even .
A revised pathway (the reductase-dependent pathway) by which polyunsaturated fatty acids are β-oxidized is presented. This pathway requires the involvement of a NADPH-dependent 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase in addition to Δ3 -cis- Δ2 -trans- enoyl - CoA isomerase and the enzymes necessary for the oxidation of saturated .TIBS 12 - October 1987 403 Beta-oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids: a revised pathway Horst Schulz and Wolf-H. Kunau are ~.o.udzzed~s presented 7hts pathway requwes the mvolvemem of a NADPH-depmdm: 2,~l-CoA reductme m addmon to A3-cis-AZ-trans-moy/-CoA tsomemse and the enzymes naxuary for the o~on of =~.rauzl fauy .Schematic diagram of fatty acid transport and beta-oxidation in the mitochondria. Click on image to enlarge. ATP synthesis . Acetyl-CoA generated by the beta-oxidation pathway enters the mitochondrial TCA cycle, where is further oxidized to generate NADH and FADH 2.The NADH and FADH 2 produced by both beta oxidation and the TCA cycle are used .
For the Mouse gene set with the same name, see REACTOME_MITOCHONDRIAL_FATTY_ACID_BETA_OXIDATION. Standard name. REACTOME_MITOCHONDRIAL_FATTY_ACID_BETA_OXIDATION. Systematic name. M14690. Brief description. Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Beta-Oxidation. Full description . Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a major public health problem worldwide. NAFLD (both simple steatosis and steatohepatitis) is characterized by alterations in hepatic lipid metabolism, which may lead to the development of severe liver complications including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Thus, an exhaustive . Donate here: http://www.aklectures.com/donate.phpsite video: http://www.aklectures.com/lecture/oxidation-of-unsaturated .
beta oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids|how does beta oxidation work
PH0 · saturated fatty acids quizlet
PH1 · how to increase fat oxidation
PH2 · how does beta oxidation work
PH3 · fatty acid oxidation pathway
PH4 · Iba pa